Nx Module Federation Technical Overview
Nx's Module Federation support is provided through a mixture of executors and the withModuleFederation() util that is used in you webpack.config file. Understanding what is happening under the hood can help when developing applications that use Module Federation as well as debugging any potential issues you run into.
What happens when you serve your host?
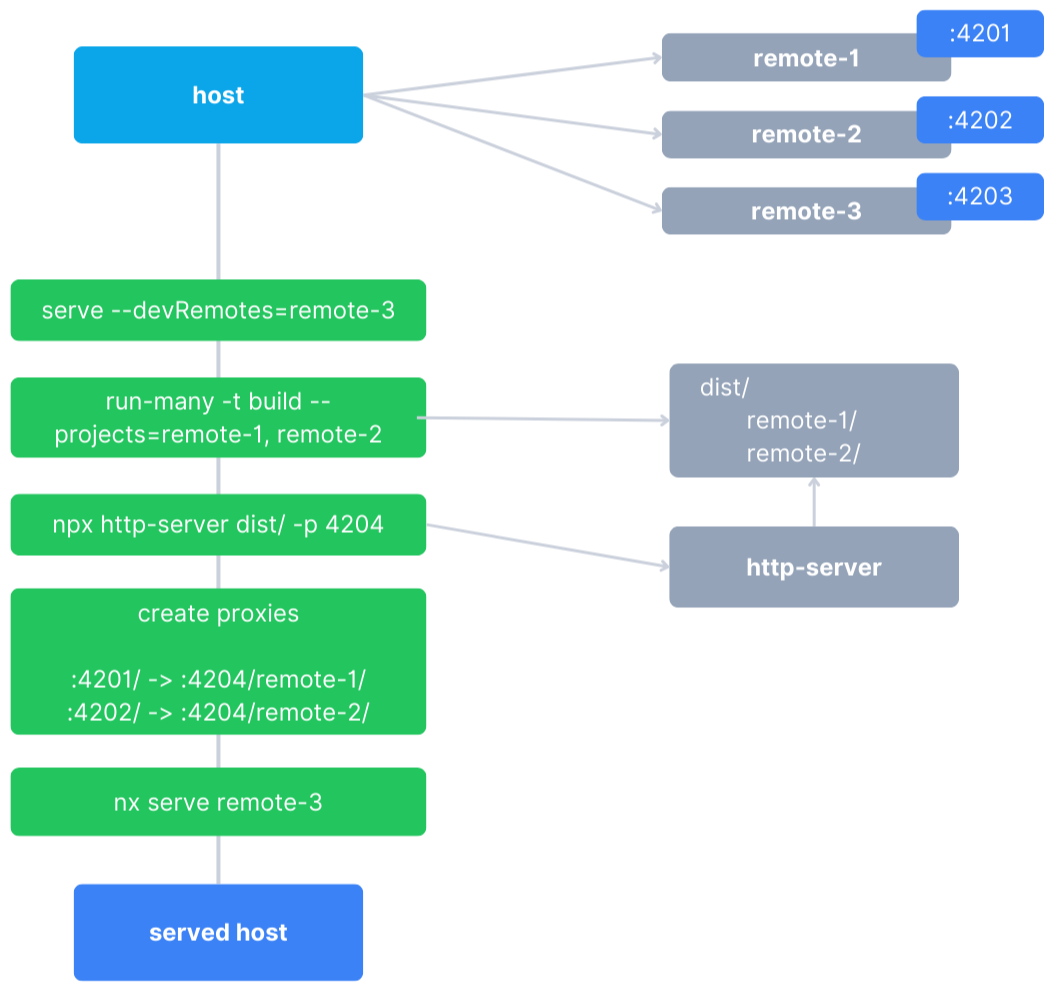
When you serve your host application via nx serve host, the Nx module-federation-dev-server executor is invoked. This executor does a few things that aim to provide a more holistic local development while ensuring a great DX (development experience).
The same technique outlined below also applies to the module-federation-ssr-dev-server.
This is important to know when it comes to deploying your SSR Module Federation application as it indicates that you can place the build artifacts from the remotes onto something like an AWS S3 Bucket and your host will be able to find these files correctly.
The executor does the following:
- Finds all the
remotesthat thehostdepends on. - Determines which
remotesneed to be served statically and which need to be served viawebpack-dev-server. - For the
static remotes, it will invokenx run-many -t build --projects={listOfStaticRemotes}. - If required, it will move the built artifacts of each
remoteto a common directory. - It will run
http-serverat the common directory such that those files are available on the network from a single port. - It will create proxy servers via
expresslistening on the ports where eachremoteshould be located (as configured in the host'smodule-federation.config.tsormodule-federation.manifest.jsonfile).- These proxy servers will proxy requests from the server to the
http-serverto fetch the correct files as requested by Module Federation.
- These proxy servers will proxy requests from the server to the
- If the
--devRemotesoption has been passed, it will serve eachdev remoteviawebpack-dev-serverallowing for HMR and live reloading when working on those remotes. - It will serve the
hostviawebpack-dev-server.
If you prefer diagrams, the one below outlines the above steps.
The NxRuntimeLibraryControlPlugin
Previously, when using shared workspace libraries as part of your Module Federation application, there was a chance that the workspace library would be provided by one of the static remotes. This would cause issues where changes to those shared libraries would not be reflected in the locally served application.
To combat this issue, we developed the NxRuntimeLibraryControlPlugin. This is a Runtime Plugin that will ensure that workspace libraries are only shared via any active dev remote. This means that any changes to the shared library will be picked up by webpack-dev-server and, as such, reflected in the locally served application.
This plugin is enabled by default, however, you can turn it off in your module-federation.config file:
1export const config: ModuleFederationConfig = {
2 ...,
3 disableNxRuntimeLibraryControlPlugin: true
4}
5